“THE trace of steam is an external pipe heating system, equipment and instruments, using water vapor. The main purposes of this system are to freeze protection and process temperature maintenance.“
currently, It has wide use in industrial units, comprising onshore and offshore drilling and production facilities, process areas, utility areas, storage parks, terminals, supply bases, auxiliary installations, pipeline stations, refineries, as, in other industrial areas.
For you who would like to understand a little more about the Steam Trace, a Scooter set up a glossary terms used during the delimitation of a steam tracing project.
GLOSSARY
External Heating
Heating using water vapor tubes disposed outside the pipe, equipment or instrument to be heated.
Equilibrium Temperature
The equilibrium temperature is obtained when the heat supplied by the heating system equals the heat lost to the environment, this condition is reached when the system enters a permanent regime and in the condition of no product flow.
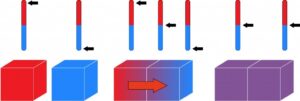
See the example below where two bodies at different temperatures exchange heat with each other until they reach thermal equilibrium.
Heating Branch or Steam Trace
Small diameter line, disposed externally to the pipe or equipment, with the function of promoting the heating of pipes, equipment and instruments, among them stand out:
- Straight Heating Branch
Features straight configuration and parallel to the pipe.
- Helical Heating Branch
Features propeller-shaped configuration, coiled externally to the pipe or equipment.
Steam Supply Trunk
Piping from which the various steam heating branches are fed.
Supply Branch
Intermediate piping that connects the supply trunk to heating branches.
Condensate branch
Small diameter line that transfers the condensate collected in the purge system to the collection trunk or main condensate trunk.
Condensate Pickup Trunk
Piping where condensate is discharged by heating systems.
Heating system (TO)
System made up of supply branches, heating and purge system, in this stand out:
- Conventional Heating System
System for which heat transfer takes place, basically, by direct contact of the heating branch with the piping.
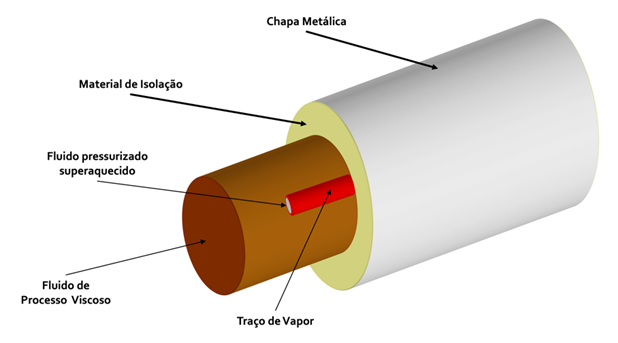
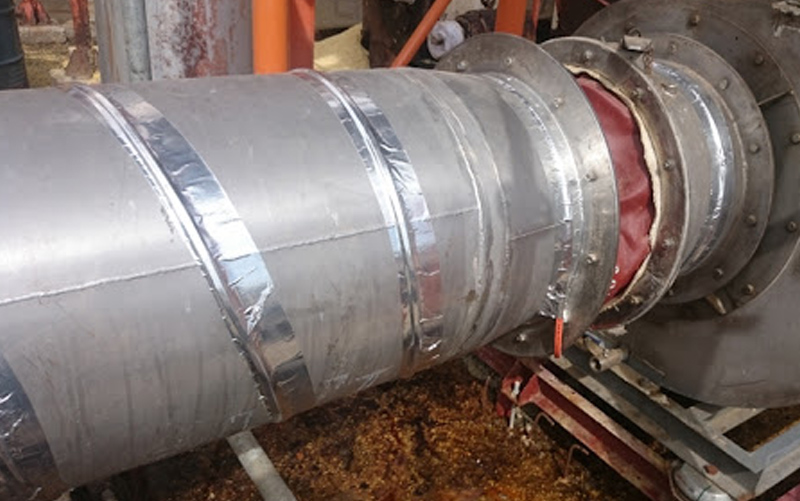
- High Performance Heating Systems
Systems for which the heat transfer from the vapor trace to the pipeline is significantly increased, making it possible to obtain temperatures closer to that of steam. Stand out: aluminum profile system, see photo below:

Heating Steam (will)
Saturated or overheated water vapor in the heating fluid
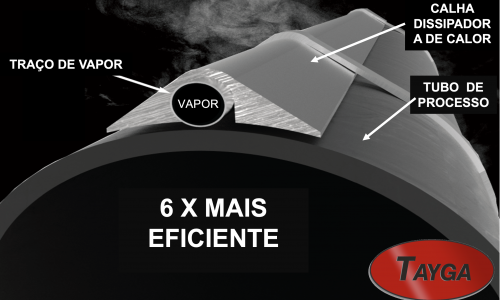
Aluminum profile
Profiled part, made by extrusion, used to connect the heating branch to the piping, in order to increase heat exchange by thermal conduction, with the aluminum trough in special alloy, the steam trace increases its efficiency by up to six times more.
Thermally conductive mass
Thermally conductive mass, also known as HTC (Heat transfer Compound), is a mass of high thermal conductivity used to increase the transfer of heat by conduction, between 2 surfaces, important to mention that this dough should not be used alone, as the main transfer element, it must be accompanied by the aluminum rail.
Basic Continuous Trace LengthO steam
Tube length measured from the stop valve to the trap.
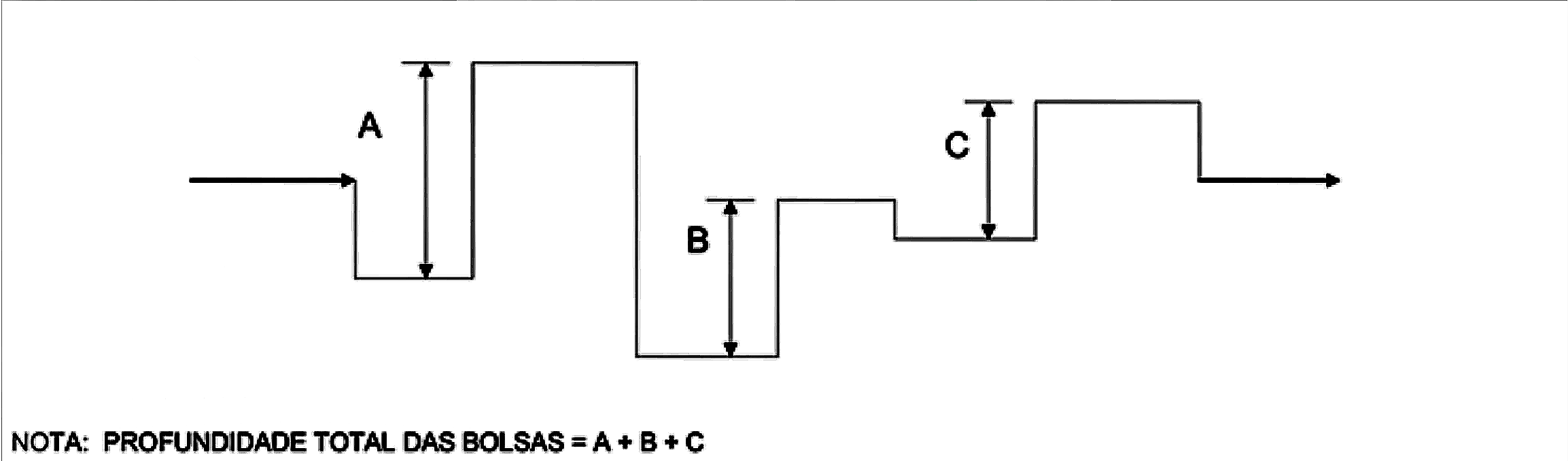
Pouch Depth
It is understood as the vertical distance, measured between successive low and high points on a heating branch, flow direction.
If you want to understand more about the steam trace, visit our website:
Trace of Steam – Site Tayga
To find out more about other heating and insulation systems, we recommend reading our complementary materials (just click and you will be redirected):

To understand how Tayga can help your industry and learn about our projects, between me contact by website (on here), fur e-mail daniel@taygahs.com or at phone and WhatsApp (21) 9.8819-3687.


